How to Do Entity SEO
If you want to know how and why you should integrate entities and entity SEO into your day to day tasks, this is the right post for you.
I've spoken recently about entity SEO in a webinar by SE Ranking [slides here] and the reason I picked that topic is that I felt there are so many "chatter" and talk about entities and little information about the impact and how to. That's why I decided to dive into it so read on.
Table of Contents:
- What is an Entity in SEO?
- Example of how Google uses Entities
- Entity SEO Vs. Keyword Research
- How to find Entities for SEO (Entity SEO Tools)
- How to Incorporate Entities in Your SEO Workflow?
- Create a Topical Map
- Entity SEO Case Study
- Recommended resources & further reading
What is an Entity in SEO?
An entity is a thing or concept that is singular, unique, well-defined and distinguishable. For example it can be a person, a place, an item, an idea, an abstract concept, a concrete element.
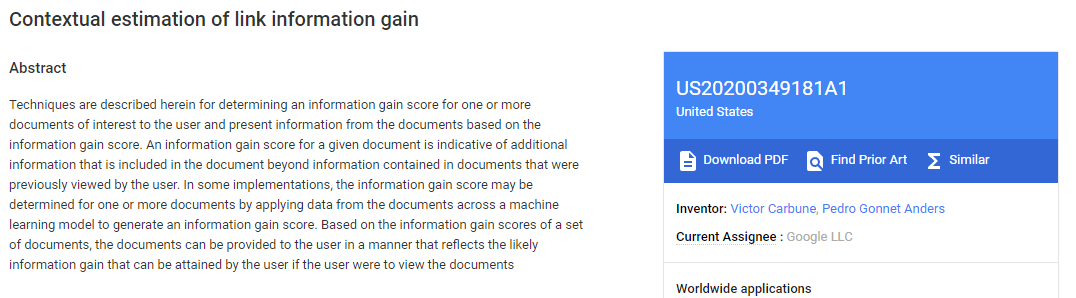
The best definition I found about entities is the one in this Google patent:
So entities are anything that is singular and can be described as a noun, linguistically.
Background
**Skip this part if you're not interested in an SEO history lesson!**
Early Google Updates
10 years ago (or more), the search results were cluttered with "spammy content" and hacks that helped undeserving pages to rank. Tactics like keyword stuffing, thin content, cloaking, copied content, content farms and other spammy tactics were utilized and they actually worked. And that was the problem.
Google decided to address this to reward more helpful useful content and punish spammy less valuable content. To do this, Google had to move away from tactics that can be manipulated easily and therefore had to move away from deciding the relevance of content based on keyword density to actually understanding and evaluating the content in more advanced ways.
This was to be able to return to the user the most related high quality results as well. So for one reason, Google wanted good results in SERPs, and another is that Google wanted to be able to better match the user query with most relevant result.
The Panda Update 2011
Many updates (which we now call systems) have been released, one of the biggest if not the biggest updates in SEO history was the 2011 Panda update. It drove websites out of business, that's how big the impact of this update was.
What was the main purpose of Panda update?
The Panda update was designed to reduce the rankings for low-quality sites (“sites which are low-value add for users, copy content from other websites or sites that are just not very useful”) and reward better rankings to high-quality sites (“sites with original content and information such as research, in-depth reports, thoughtful analysis, etc.…”)
The Penguin Update 2012
And while the SEO industry was still recovering from the Panda update, Google stroked again with the 2012 Penguin update, aka the web spam algorithm update.
What did Penguin update do?
The Penguin update was created to help reduce the number of sites appearing in SERPs that were using black hat SEO techniques to manipulate results with link schemes. Again, this update also shook the industry.
The Knowledge Graph
In that same year, Google introduced the knowledge graph. The knowledge graph is a knowledge base used by Google to store and understand entities and the relation between them. With the launch of the knowledge graph, Google announced moving away from "strings" to "things", which basically mean more emphasis will be given to entities and the relationship between them over just keywords.
Another definition I found is this for knowledge graphs is this:
A knowledge graph can look a something as simple as this:
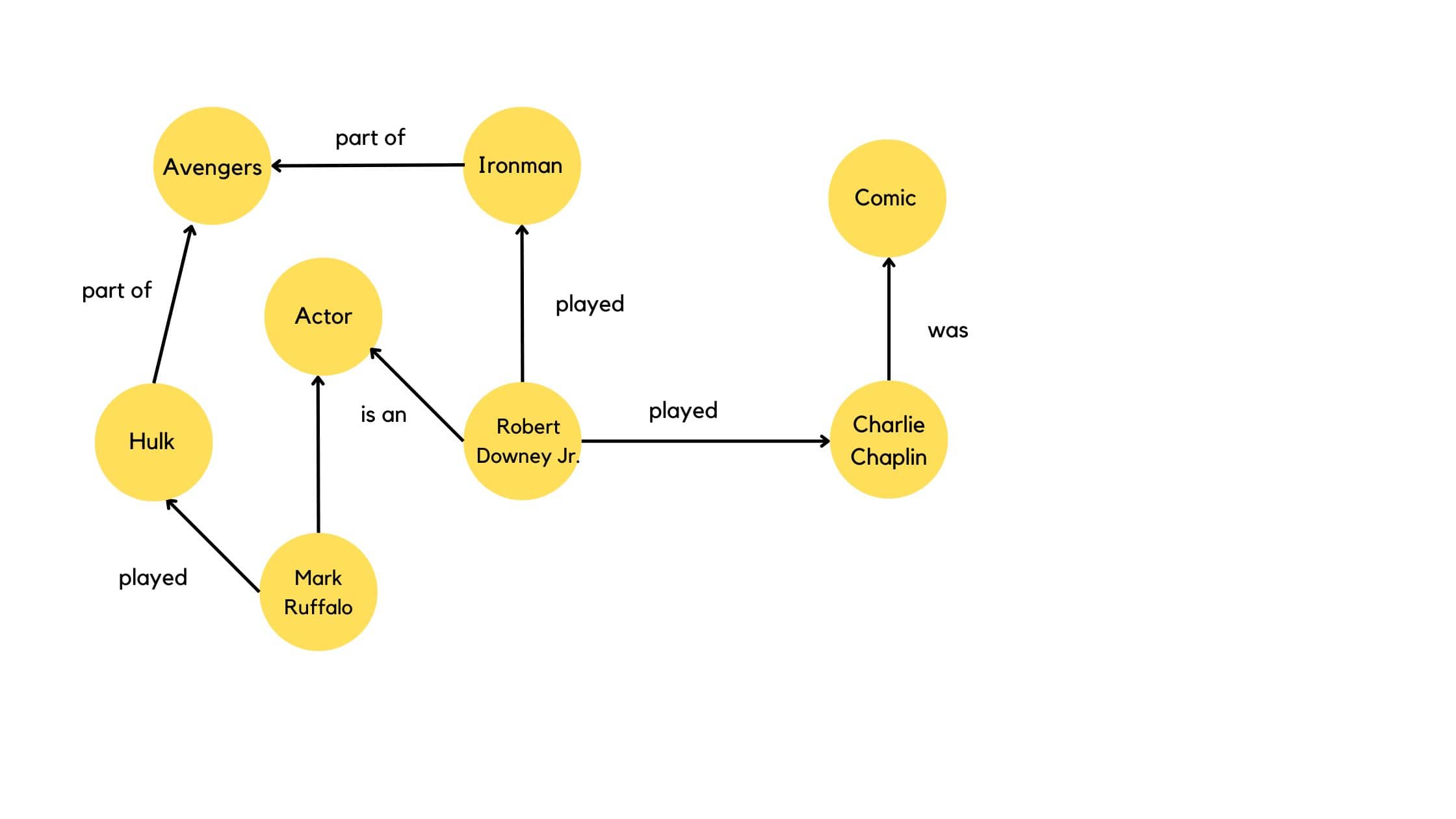
- Each yellow circle in this graph represents an entity and the lines represent the relation between those entities.
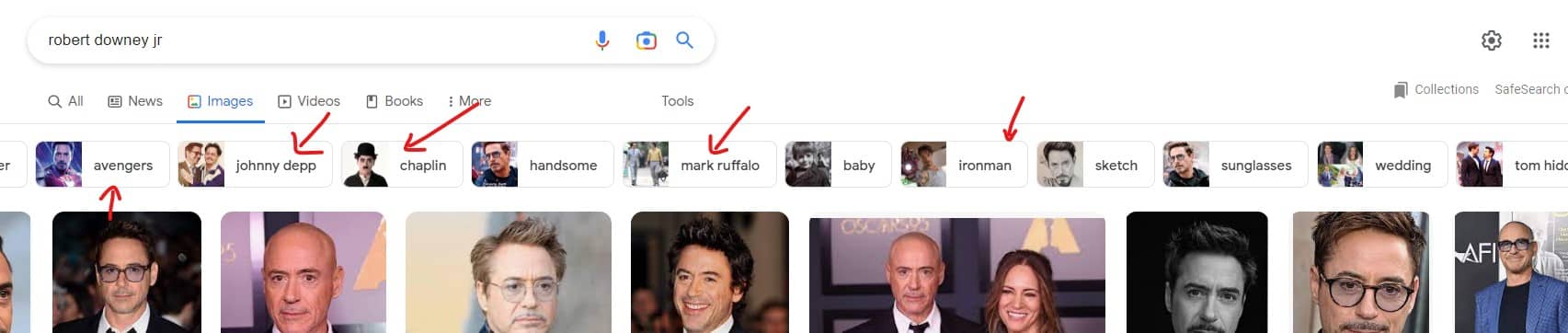
- If you use Google image search for "Robert Downey Jr" you'll see google suggesting plenty of related entities based on Google's knowledge graph. Here's what I got in Google image search:
So in conclusion, every piece of information online, is taken by Google and converted into part of its knowledge graph (t&c apply :)) Here's an example of how a text can be converted to a graph:
Why do we need to think about Entity SEO?
Because Google now evaluates results not based off keywords only, but also entities and the relationship between them. That's how the search works and therefore how we should be thinking and optimizing.
Example of how Google uses Entities
In SERPs, when you click on the 3 dots next to a results you get "about this result". There was a time when Google showed information about related search terms in "about this result" (doesn't do so any more).
Here's an example of how Google used entities to evaluate a search result (source):
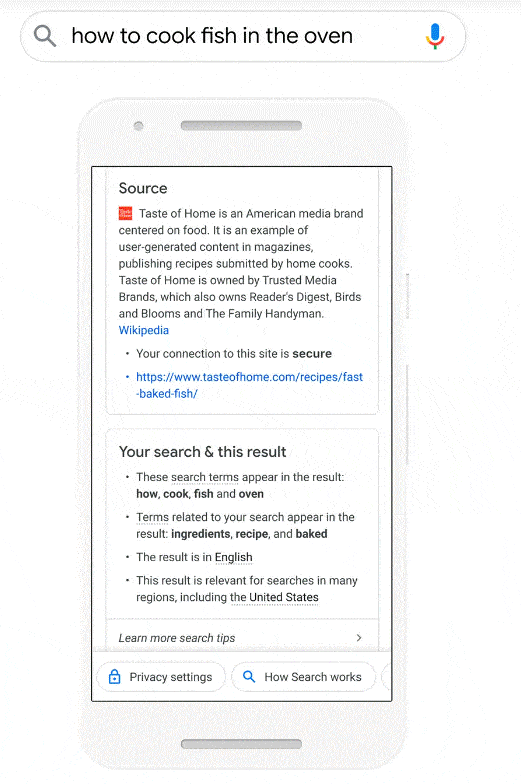
While the search query was "how t cook fish in the oven", Google showed other related entities like "recipe" are one of the reasons you see this result. You cannot write instructions about "how to cook fish in the oven" without talking using the entity "recipe" in your content and therefore, Google sees the inclusion of "recipe" entity in your content as important. So Google needs to see that you have the entities related to your topic/blog present in the content.
What does using entities mean for SEOs?
Ok so we understand that entities are important but how will this impact our day to day work as SEOs? here's how:
- Spelling: while you should the right spelling to localize your content for your target audience (colour vs color), rest assured that Google understands that both represent the same "thing".
- Keyword Metrics: Density; The repetition of exact match keywords “buy shoes online” all over the content is less important. Keyword volume also matters less since Google understands that both puppy and dog are the same thing so it doesn't matter which has a higher search volume if you're trying to decide which to use in your content (note: you should use both).
- Variations: Google understands that a puppy is the same thing as a dog, so using either or both in content is totally fine. Same as with things like “robert downey jr” & “rdj”.
- Topical Authority: Topical Authority can be achieved by focusing on entities rather than keywords, as one cannot exist without the other.
Entity SEO Vs. Keyword Research
I think the best way to understand this, is to see an example!
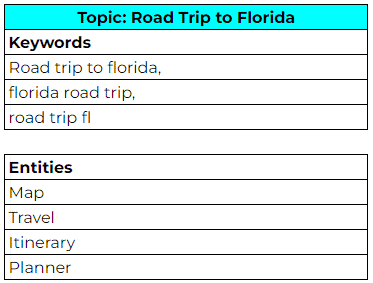
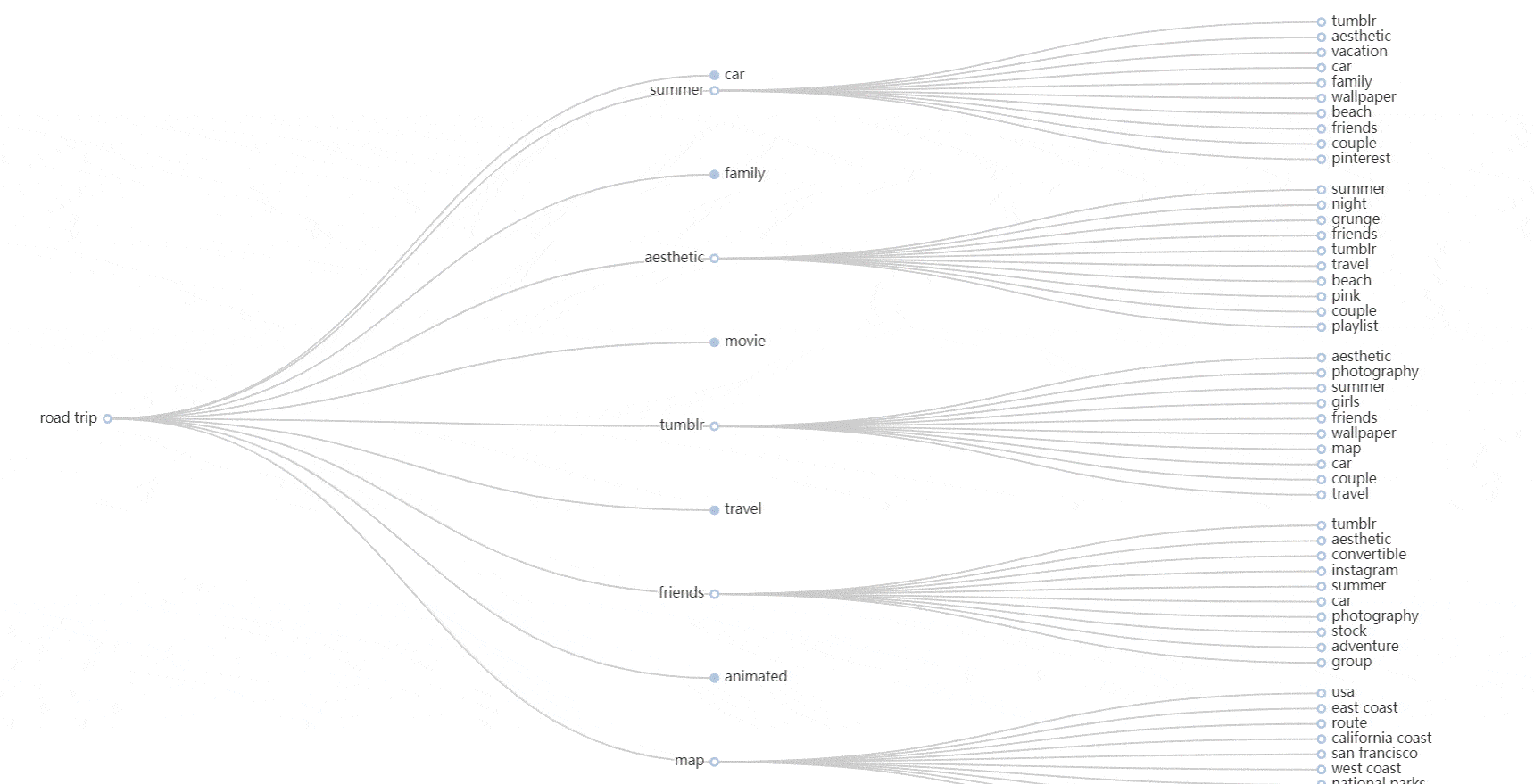
- In the example above, we're doing the usual keyword research for "road trip to Florida". But we're also adding related entities.
- Unlike keywords, entities don’t have to include the same words as the main topic.
- Simple right? So how to find entities?
How to find Entities for SEO (Entity SEO Tools)
There are many ways using tools (and without tools) that you can find entities related to your content.
Here are a list of tools that you can use to find and analyze entities
- Google Image Search
- Google Trends related queries and related topics
- Data from autocomplete and search suggestions
- Wikipedia. Search for your main entity on Wikipedia and find related entities and topics on that page.
- Google Knowledge Graph to pull relevant entities
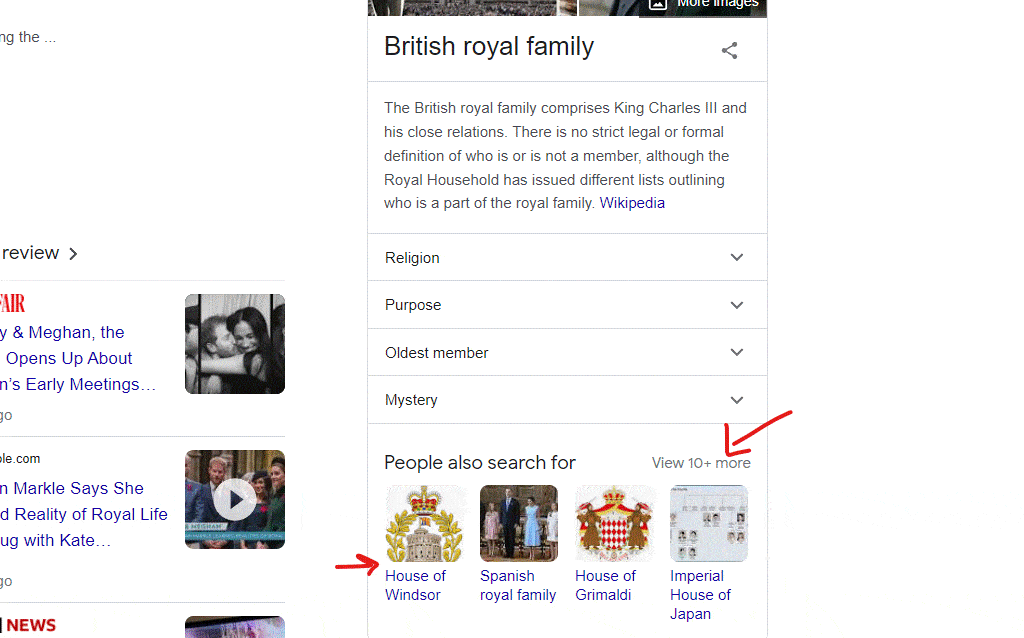
6. Google Knowledge Graph Search API
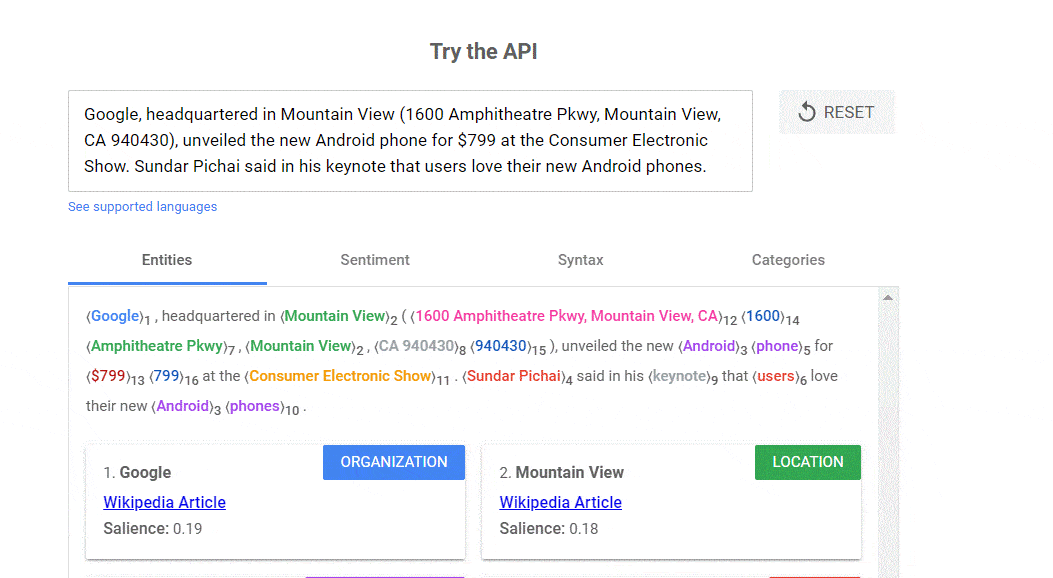
7. Use non-web resources. Brainstorm, read... some things can be done without tools
8. InLinks (which is the only SEO Company focused on semantic SEO, I recommend you check their technology, full disclosure, I'm affiliated with them as they offered me a free account).
9. Topically.io which relies on Google image search to pull all the related entities.
11. textrazor.com/demo
How to Incorporate Entities in Your SEO Workflow?
If you're wondering "all of this is great Sara, but how do I incorporate that into my daily SEO tasks?" here's a step by step guide to adding entity SEO tasks into your daily workflows.
1. Create a Topical Map
So it all starts when you want to update or create new content. The first step when working on a website from a content standpoint is to create a topical map.
What's a topical map in SEO?
A topical map is a map of subtopics that are related to the main topic of your website. It's useful to create a topical map to understand where page(s) fall and what topics have been covered and what have been missed. A topical map helps you achieve topical authority.
How to create a topical map in SEO?
I've discussed this in details in my guide to doing a content audit. I highly recommend you check it out.
A topical map can look as simple as this:
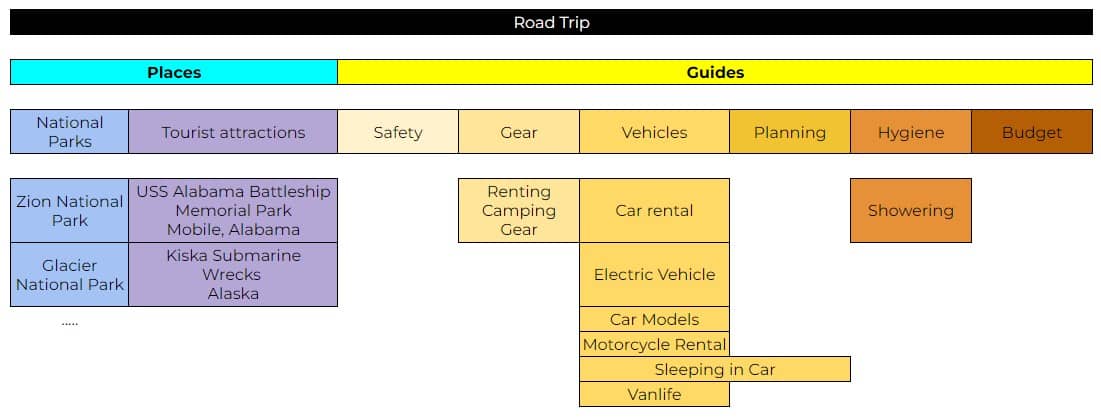
** please note that this topical map is not comprehensive and more related topics can be added.
2. Prioritize your topics
Once you have a topical map, decide on which topics are more important for you and therefore which pages you want to update/create first.
For this example, let's say we want to address "Zion National Park" first. We decided that this topic can be covered with 1 blog post. Some topics may require multiple blog posts. For example if your topic is "SEO", it's very challenging to cover that in one blog post.
3. Do keyword and entity research
So for "Zion national park", we need to do entity research. We'll use the tools and tactics discussed earlier. Now you should end up with a list of related entities. You may want to draw that into a mini entity graph for visualization purposes. (note the graph in the image below is not comprehensive)
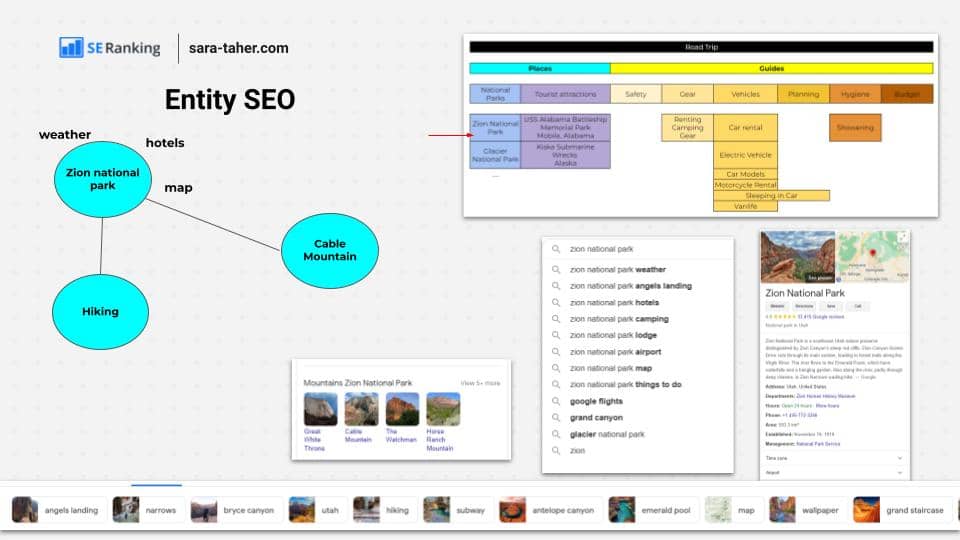
Do your usual keyword research. Here's the outcome of your work:

Now you're ready to optimize your content!
4. Schema
There's a common misconception that schema is used only for getting rich results in SERPs. Schema is also used to communicate to Google what a page is about. Using it to markup entities existing on a page helps Google have a better understanding of page content and therefore may help it perform better in search.
Note:
- Use mainEntity if the webPage is about a specific entity.
- You may also want to add schema referring to other entities on the page as if there’s no schema.org type for your entity.
Here are some example schema codes. These codes can be automatically generate using tools like inlinks, I have not tried using any other SEO tool to generate this type of schema except inlinks, it automates the process very well so far from what I've seen. You may also try to generate this schema code manually and validate it with the structured data testing tool. Now to the examples:
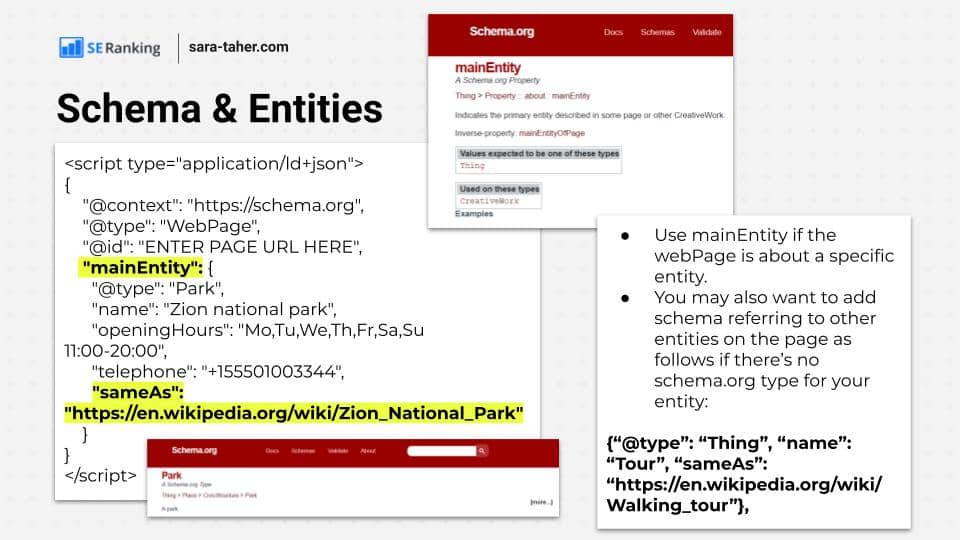
In the above example you can see the "main entity" schema which is used to communicate to google the main entity this page is about. In our example, "zion national park" has a wikipedia page, and there's also a park schema type in schema.org. This is the perfect example. So we communicated to Google that the main entity of this page is a "park" and it's the same park as the "zion national park" wiki page.
What if the main entity of the page does not have a schema.org type? in that case we use this code (example code below for a page about tours):
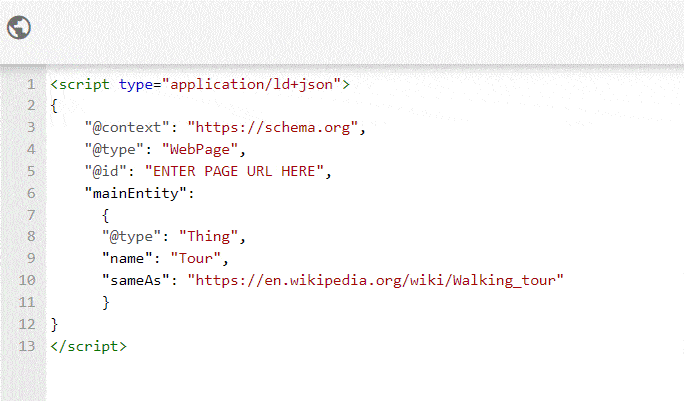
In addition to the "main entity" schema, you can also include other schemas to show other secondary entities on a page. Example:
5. Internal linking
Last but never least internal linking. Make sure you follow internal linking best practices and link to entities consistently. Nothing new here, same old internal linking tactics. Maybe I'll write a separate blog post about that.
Entity SEO Case Study
The best and most simple case study I came across to show the impact of entity SEO on the overall performance of a website is the one I found here. Here's a summary:
- This was a local SEO client.
- Google maps was used to find and note any key local entities, such as state parks, lakes, or other features in the area of the client business.
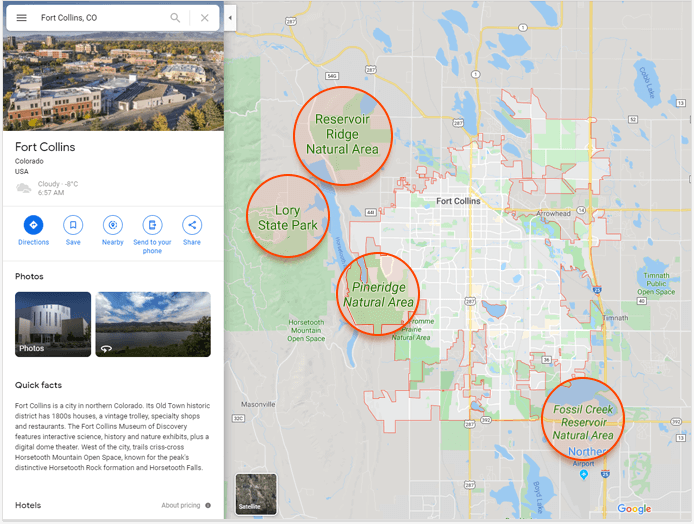
- Created and edited content by referencing landmarks as well as adding driving directions from to the client location from famous landmarks. Example:
"XYZ Contractor is located in Old Town Fort Collins, just east of Horsetooth and minutes from Colorado State University..."
- The website received 32% lift by simply adding geographically relevant terms to the page and linking to driving directions.
To make this post the most comprehensive there is, here's a very valuable video from Mary Hayes about entity SEO:
Recommended resources & further reading
There are so many more you can learn about entity SEO. So here's a list of recommended readings:
- https://www.seobythesea.com/
- https://www.holisticseo.digital/
https://www.link-assistant.com/news/entity-case-study.html - https://patents.google.com/patent/US20160371385
- https://starling.social/blog/post/143/entity-first-seo-strategy
- https://support.google.com/programmable-search/answer/9350760
- https://inlinks.net/p/insight/why-is-no-one-talking-about-entity-seo/
- https://minuttia.com/entities/
- https://kalicube.com/learning-spaces/faq/brand-serps/entity-home-in-seo-explainer/
- https://wordlift.io/blog/en/seo-case-studies/
- https://www.infront.com/blog/the-ultimate-guide-to-entity-seo-an-introduction-to-entity-based-seo/
- https://beanstalkim.com/learn/articles/patent-ranking-search-results-based-on-entity-metrics/
- https://searchengineland.com/see-entities-web-page-tools-help-194710
- https://wordlift.io/blog/en/content-hub-seo/
- https://searchengineland.com/semantic-search-entity-based-search-388221
The SEO Riddler Newsletter
Join the newsletter to receive the latest updates in your inbox.