Insights From the Google DOJ Documents (Part 2)

Hello Riddlers!
Last week we dug a bit into some of the DOJ lawsuit documents against Google, and found some very interesting insights (read it here). But actually... there's more 😄 Who knew it would be that fun to work in SEO!
TL;DR
- I didn't know that open AI has it's own search index (or building one)!
- If you want to get cited in AIO, you need to understand fast search better. What's that? keep scrolling 👇😎
- OpenAI previously sought out a partnership with Google for grounding, but Google declined (hahahaha.... 😂)
- LLMs are not fit to replace search... YET.
- Google is the place for navigational queries.
- Page quality measures rely mainly on the webpage.... 🤷
- Court documents shed more light on the data used in rankings. Glue, Navboost, and RankEmbedBERT (you'll have to scroll below to learn more 😅)
- I've raised this observation before on all LLMs, Google does not use click-and-query data to pre-train its base Gemini models.
OpenAI has it's own search index!
We've all heard the terms "grounding" no, not grounding coffee, the other one... LLM grounding 😄 and "RAG"
- Grounding is the process of connecting LLMs to an external data source to provide more accurate results and anchor their answers in reliable sources and citing real-world information.
- Through the grounding, the user prompt is converted to search queries ( query fan out) that are sent to a search engine and then incorporate information retrieved into the output of the LLM.
- GenAI products treat search results as fact, so the quality of search results directly impacts the quality of GenAI responses. This means that both Google, and LLM platforms need to continue to provide an incentive for publishers to generate high quality content. How? No idea... but how about some clicks 😄
- But here's the thing part, according to the court documents, OpenAI built it's own search index:
"Successful grounding in search requires a high-quality search application program interface, or API. See id. at 392:11–394:16 (Turley) (discussing quality issues with third-party search providers, which compelled OpenAI to build its own search index"
- I'm not sure how this fits in, given that we know multiple tests have shown that ChatGPT is using Google search results.... is this temporary? are they using a mix?
Google Fast Search
Gemini's grounding process includes the use of "Fast Search". Here's what we know about Fast search from the court document:
"FastSearch is based on RankEmbed signals—a set of search ranking signals—and generates abbreviated, ranked web results that a model can use to produce a grounded response. Id. FastSearch delivers results more quickly than Search because it retrieves fewer documents, but the resulting quality is lower than Search’s fully ranked web results."
AI Overviews also relies on Fast search... this explains the discrepancies we see between search results and sources cited in AIO. If you want to get cited in AIO, you need to understand fast search better.
Here's a refresher from last week's blog of how AI Overviews are generated:
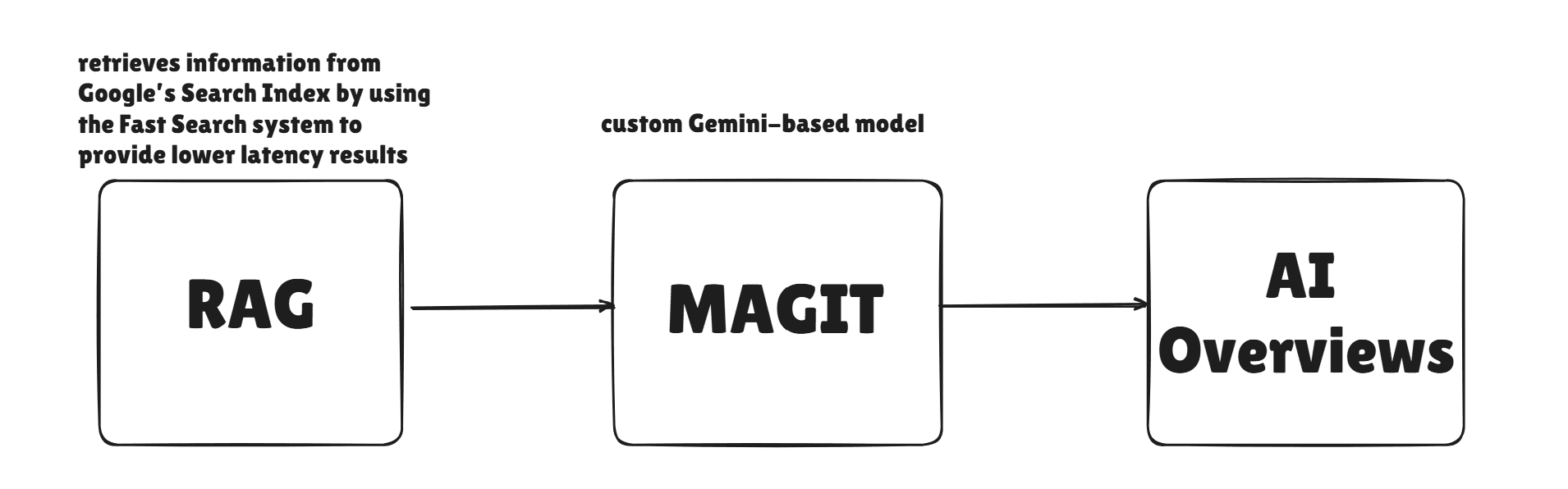
FastSearch is based on RankEmbed signals which is faster because it retrieves less documents, but that also mean lower quality. We can safely conclude that results cited in Gemini or AIO can be "lower quality".
OpenAI previously sought out a partnership with Google for grounding, but Google declined
Woooooooooow...
Google knows that they have a superior search platform, that is the most prepared to fight spam and return high quality results (in the grand schema of things and despite all the crazies we see in search results sometimes, this is still true).
Here's an instance I came across recently where Google is recommending I search elsewhere 😄
LLMs are not replacing search yet
"ChatGPT already expanded what is possible for parts of Search, but users don’t yet use ChatGPT for the full range of Search needs"
This is another way to say that search and Google both are still kings. Why? because Chatgpt and co have not replaced the usual parts that make up regular search.
Google is the place for navigational queries
When users want to go to a specific website or brand, they will use Google not AI products. approximately 12% of Google searches are navigational.
What does this mean for SEO?
- The boring advice: build a strong brand users search for
- Give special attention to your bottom of funnel conversion pages, to make sure that wherever the user goes... they end their journey with us, on our websites. [Read more about the importance of bottom of funnel pages in today's search landscape]
Page quality measures rely mainly on the webpage
In the court document, Google claims that, when it comes to "quality measures including authoritativeness" of a webpage, these are influenced largely by metrics other than user interactions and data.
This is a bit confusing, as Google referred to "user interactions" as the Google magic. See previous court documents below:

Moving on, the document also mentions that
- Some of Google’s quality sub-signals are scale dependent
- Most of Google’s quality signal is derived from the webpage itself
Data used in rankings
The court document revealed/explained a lot of information about different systems used in ranking and qualifying URLs.
- Glue data: a super search log that tracks a lot of details about a search and how people use the results. It collects information:
- About the search itself: the words typed, the language, the user location, and what device they’re on.
- About the results shown: the top 10 links and any extra SERPs features like images, maps, People Also Ask, or a Knowledge Panel.
- About user actions: what people click on, where they hover, and how long they stay on the SERPs.
- About query understanding – spelling fixes, related terms, and suggestions.
- Navboost data: Navboost is a “memorization system” that aggregates click-and-query data about the web results delivered to the SERP. It is an important component of the Glue data, and like Glue it can be thought of as a giant table.
- RankEmbed and later RankEmbedBERT are Google’s ranking models. They use two main types of data:
- Search logs – information from real user searches collected over 70 days (the exact percent used is hidden).
- Human ratings – scores given by human reviewers, which Google uses to judge how good the search results are.
- Together, these help the models learn which results should appear higher or lower in search.
Google does not use click-and-query data to pre-train its base Gemini models
This is another reason why there's a discrepancy between what we see in Gemini, AI Overviews, on one side and in search on the other side.
HOWEVER, Gemini (similar to chatgpt) is trying to collect user feedback on the Gemini model itself. And therefore, once again, this is another reason why there are discrepancies between the 10 blue links and Gemini, Chatgpt, and AI Overviews.
And That’s a Wrap (Almost 😄)
Obviously the court documents are way longer than what I have summarized here and included way more points that what I highlighted.
I didn't use AI to go through them as I was looking for accuracy and my own insights and not the AI's. That said, I still recommend you skim through them.
Here you go:
Hope you found this useful and see you next newsletter!
Like what you read and want to support me?
- Sign up for my newsletter if you're not already.
- Share the newsletter and invite your friends to signup. Help me reach 2k signups by end of 2025 please 🙂
- Provide feedback on how I can make this newsletter better!!!
- Buy me coffee.
- If you're an SEO tool or an SEO service provider, consider sponsoring my newsletter. I'm also open to other partnership ideas as well.
Disclaimer: LLMs were used to assist in wording and phrasing this blog.
The SEO Riddler Newsletter
Join the newsletter to receive the latest updates in your inbox.